Contents
%%Uso de formato largo: mejores soluciones format long
Ejercicio 1
x = [10; 20; 40; 60; 80]; y = [x, log(x)]; fprintf('\n Numero Natural log\n') fprintf('%4i \t %8.3f\n',y')
Numero Natural log 10 2.303 20 2.996 40 3.689 60 4.094 80 4.382
Ejercicio 2
A = [4 -2 -10; 2 10 -12; -4 -6 16]; b = [-10; 32; -16]; disp('Solucion') x = inv(A)*b disp('Comprobacion') A*x - b %prueba
Solucion
x =
2
4
1
Comprobacion
ans =
0
0
0
Ejercicio 3
A = [4 -2 -10; 2 10 -12; -4 -6 16]; b = [-10; 32; -16]; disp('L U') [L U] = lu(A) disp('Solucion') x = inv(U)*inv(L)*b disp('Comprobacion') A*x - b %prueba
L U
L =
1.000000000000000 0 0
0.500000000000000 1.000000000000000 0
-1.000000000000000 -0.727272727272727 1.000000000000000
U =
4.000000000000000 -2.000000000000000 -10.000000000000000
0 11.000000000000000 -7.000000000000000
0 0 0.909090909090909
Solucion
x =
2
4
1
Comprobacion
ans =
0
0
0
Ejercicio 4
A = [ 0 1 -1; -6 -11 6; -6 -11 5 ]; [x, D] = eig(A) T1 = A*x T2 = x*D
x =
0.707106781186543 -0.218217890235999 -0.092057461789830
0.000000000000004 -0.436435780471979 -0.552344770738996
0.707106781186551 -0.872871560943971 -0.828517156108490
D =
-1.000000000000005 0 0
0 -1.999999999999970 0
0 0 -3.000000000000024
T1 =
-0.707106781186547 0.436435780471991 0.276172385369494
-0.000000000000002 0.872871560943942 1.657034312217000
-0.707106781186553 1.745743121887913 2.485551468325490
T2 =
-0.707106781186547 0.436435780471991 0.276172385369494
-0.000000000000004 0.872871560943945 1.657034312217002
-0.707106781186555 1.745743121887915 2.485551468325490
Ejercicio 5
A = [(1.5 - 2i) (-0.35 + 1.2i); (-0.35 + 1.2i) (0.9 -1.6i)];
b = [(30 + 40i); (20 + 15i)];
v = inv(A)*b;
disp('Solución:')
V1 = v(1)
V2 = v(2)
S = v.*conj(b)
Solución: V1 = 3.590204703232966 +35.092792858473679i V2 = 6.015537032086641 +36.221212342138735i S = 1.0e+03 * 1.511417855435936 + 0.909175597624892i 0.663628925773814 + 0.634191191361475i
Ejercicio 6
Resuelve las torres de Hanoi function hanoi (n, i, a, f) if n > 0 hanoi (n - 1, i, f, a); fprintf('mover disco %d de %c a %c\n', n, i, f); hanoi (n - 1, a, i, f); end
hanoi(3, 'i', 'a', 'f')
mover disco 1 de i a f mover disco 2 de i a a mover disco 1 de f a a mover disco 3 de i a f mover disco 1 de a a i mover disco 2 de a a f mover disco 1 de i a f
Ejercicio 7
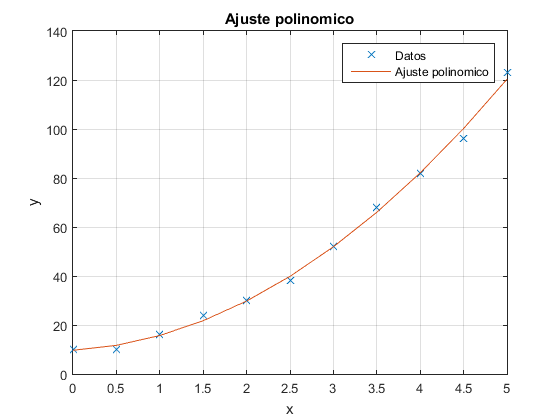
figure(7) x = 0:0.5:5; y = [10 10 16 24 30 38 52 68 82 96 123]; p = polyfit(x,y,2); yc = polyval(p,x); plot(x,y,'x',x,yc) xlabel('x'),ylabel('y'),grid,title('Ajuste polinomico') legend('Datos','Ajuste polinomico',4)
Ejercicio 8
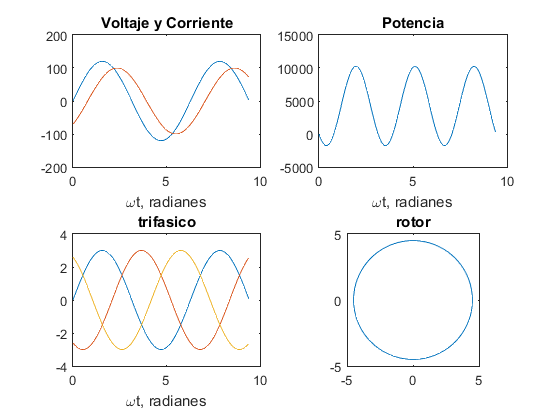
figure(8) wt = 0:0.05:3*pi; v = 120*sin(wt); i = 100*sin(wt-pi/4); p = v.*i; subplot(2,2,1) plot(wt,v,wt,i) title('Voltaje y Corriente'),xlabel('\omegat, radianes') subplot(2,2,2) plot(wt,p) title('Potencia'),xlabel('\omegat, radianes') Fm = 3.0; fa = Fm*sin(wt); fb = Fm*sin(wt-2*pi/3); fc = Fm*sin(wt-4*pi/3); subplot(2,2,3) plot(wt,fa,wt,fb,wt,fc) title('trifasico'),xlabel('\omegat, radianes') fR = 3/2*Fm; subplot(2,2,4) plot(-fR*cos(wt),fR*sin(wt)) title('rotor'),axis square
Ejercicio 9
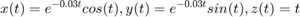
t = 0:0.1:16*pi;
x = exp(-0.03*t).*cos(t);
y = exp(-0.03*t).*sin(t);
z = t;
subplot(1,1,1)
plot3(x,y,z), axis square
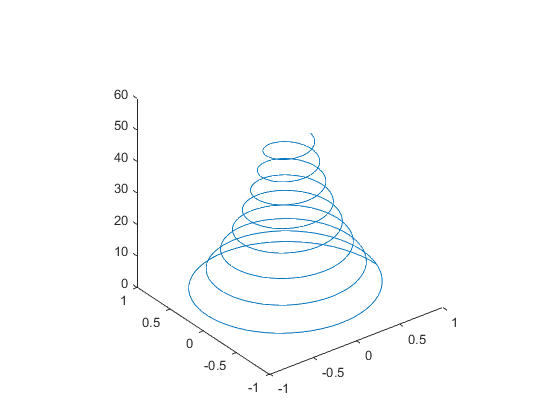
Ejercicio 10

t= -4:0.3:4;
[x,y]=meshgrid(t,t);
z=sin(x).*cos(y).*exp(-(x.^2+y.^2).^0.5);
mesh(x,y,z) , axis square
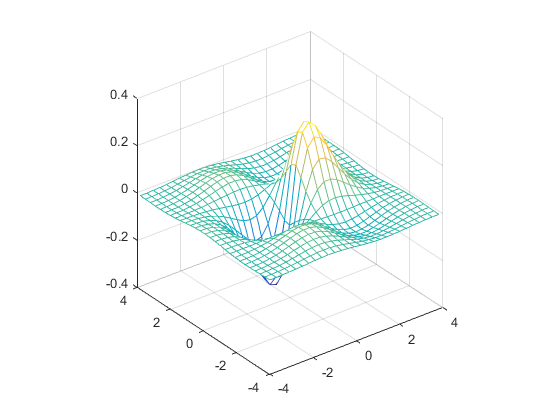
Ejercicio 11
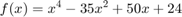
q = [1 0 -35 50 24]; %Matriz de coeficientes del polinomio disp('Raices') r = roots(q) %Raices del polinomio disp('Comprobacion') polyval(q,r) %Evaluar valores del polinomio con las raices -> [0]
Raices r = -6.491019200948975 4.870585123318113 2.000000000000000 -0.379565922369139 Comprobacion ans = 1.0e-11 * -0.141398004416260 -0.065014660322049 -0.003552713678801 -0.000355271367880
Ejercicio 12
figure(12) Ejemploode % function Ejemploode % [t, yy] = ode45(@HalfSine, [0 35], [1 0], [], 0.15); % plot(t, yy(:,1)) % function y = HalfSine(t, y, z) % h = sin(pi*t/5).*(t<=5); % y = [y(2); -2*z*y(2)-y(1)+h];
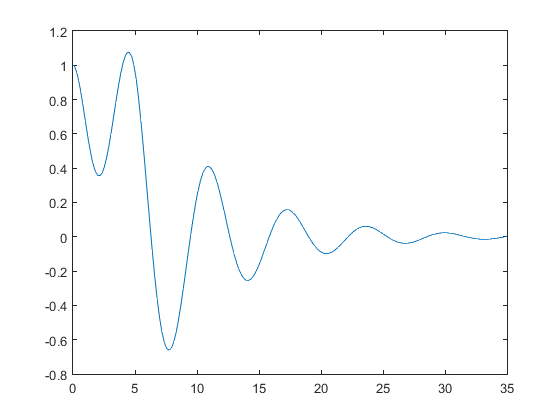
Ejercicio 13
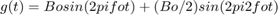
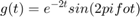
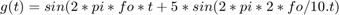
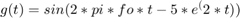
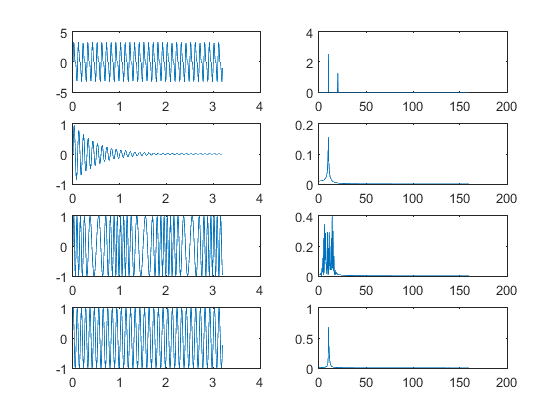
figure(13) k = 5; m = 10; fo = 10; Bo = 2.5; N = 2^m; T = 2^k/fo; ts = (0:N-1)*T/N; df = (0:N/2-1)/T; SampledSignal = Bo*sin(2*pi*fo*ts) + Bo/2*sin(2*pi*fo*2*ts); An = abs(fft(SampledSignal, N))/N; subplot(4,2,1) plot(ts, SampledSignal) subplot(4,2,2) plot(df, 2*An(1:N/2)) SampledSignal1 = exp(-2*ts).*sin(2*pi*fo*ts); An1 = abs(fft(SampledSignal1, N))/N; subplot(4,2,3) plot(ts, SampledSignal1) subplot(4,2,4) plot(df, 2*An1(1:N/2)) SampledSignal2 = sin(2*pi*fo*ts + 5*sin(2*pi*fo/10*ts)); An2 = abs(fft(SampledSignal2, N))/N; subplot(4,2,5) plot(ts, SampledSignal2) subplot(4,2,6) plot(df, 2*An2(1:N/2)) SampledSignal3 = sin(2*pi*fo*ts - 5*exp(-2*ts)); An3 = abs(fft(SampledSignal3, N))/N; subplot(4,2,7) plot(ts, SampledSignal3) subplot(4,2,8) plot(df, 2*An3(1:N/2))
Ejercicio 14
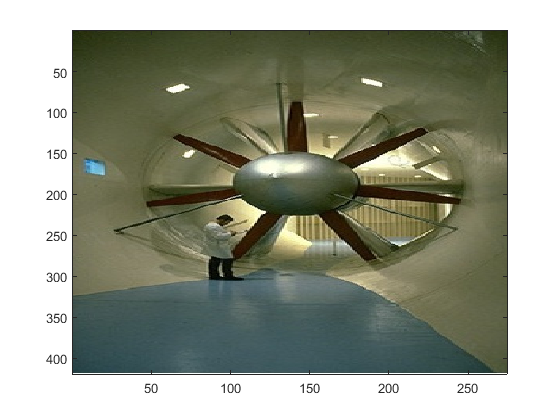
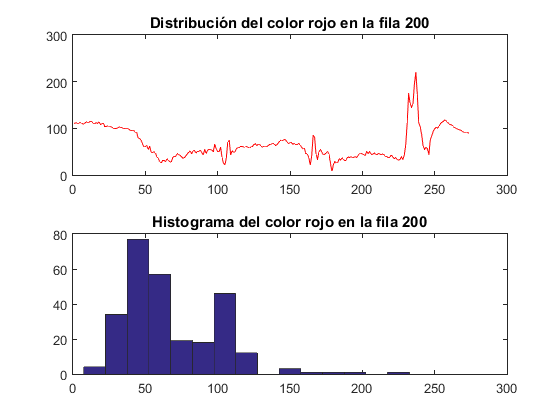
figure(14) A = imread('WindTunnel.jpg', 'jpeg'); image(A) row = 200; red = A(row, :, 1); gr = A(row, :, 2); bl = A(row, :, 3); figure(141) subplot(2,1,1) plot(red, 'r'); title('Distribución del color rojo en la fila 200'); %hold on %plot(gr, 'g'); %plot(bl, 'b'); subplot(2,1,2) hist(red,0:15:255); title('Histograma del color rojo en la fila 200');
Ejercicio 15
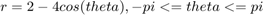
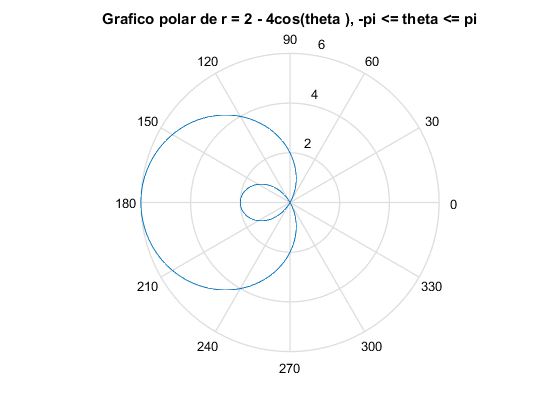
theta = linspace(-pi, pi, 180);
r = 2 - 4*cos(theta);
figure(15)
polar(theta, r);
title('Grafico polar de r = 2 - 4cos(theta ), -pi <= theta <= pi');